Nicotine Testing Understanding the Procedure and Preparation

Nicotine testing measures the level of nicotine in the body, a substance primarily found in cigarettes and other products like e-cigarettes or vapes, which can have significant health impacts. This article explores nicotine testing, its importance, duration in the body, methods such as urine and blood tests, and how to prepare for testing.
Important things about Nicotine Testing

What is Nicotine Testing?
Nicotine testing is a procedure to determine whether nicotine is present in the body. It is commonly found in smokers, users of e-cigarettes, and other products that contain this substance.
What is Nicotine?
Nicotine is an alkaloid compound extracted from plants in the Nicotiana genus. It affects the nervous system by increasing dopamine and other neurotransmitters in the brain, making it highly addictive.
Other effects on the body can include increased heart rate, high blood pressure, tolerance that leads to needing more of the substance, and withdrawal symptoms when trying to quit.
How Does Nicotine Enter the Body?
Nicotine can enter the body through several methods:
Cigarettes, tobacco, and tobacco products: This can occur through smoking or chewing. Nicotine can also be absorbed through the skin, especially for those who work with tobacco products.
Secondhand and thirdhand smoke: Secondhand smoke refers to inhaling smoke from a burning cigarette, while thirdhand smoke involves inhaling or coming into contact with residues left on surfaces after the smoke has dissipated. This includes e-cigarettes as well.
E-cigarettes containing nicotine.
Nicotine Replacement Therapy (NRT): These are products that contain low levels of nicotine, used to alleviate withdrawal symptoms in those trying to quit smoking, such as nicotine gum or patches.
Certain vegetables: Some plants, like cauliflower, eggplant, tomatoes, and bell peppers, also contain small amounts of nicotine.
Where Can Nicotine Be Found in the Body?
Nicotine can be detected in blood, urine, saliva, hair, and nails.

Why Test for Nicotine?
Pre-employment Screening: In some countries, there are campaigns to encourage smoking cessation. As part of these initiatives, some employers require nicotine testing before hiring.
Pre-surgery Screening: Nicotine reduces blood flow to organs, which can impede recovery after surgery. So, nicotine levels are often tested before surgery.
Monitoring Smoking Cessation: Measuring nicotine levels in the body helps track the progress of individuals attempting to quit smoking.
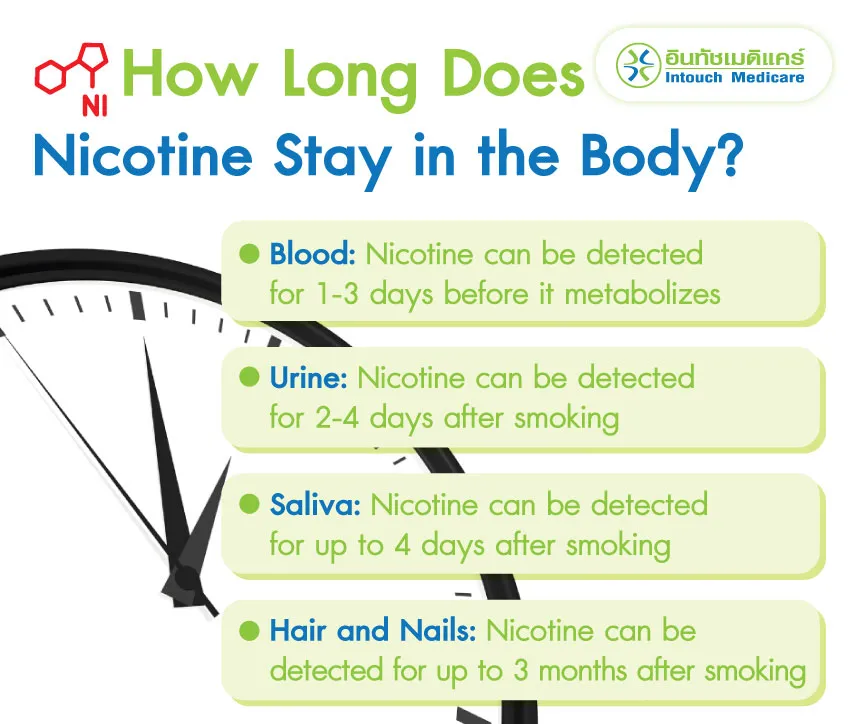
How Long Does Nicotine Stay in the Body?
Blood: Nicotine is absorbed into the blood within 10 seconds and can stay in the blood for 1-3 days. The liver then metabolizes nicotine into cotinine, which remains in the body longer and can also be tested. Cotinine stays in the blood for about 10 days after smoking.
Urine: Nicotine can be detected in urine for 2-4 days after smoking. Cotinine can be detected in urine for 2-3 weeks.
Saliva: Nicotine can be detected in saliva for up to 4 days after smoking.
Hair and Nails: Cotinine can be detected in hair and nails for up to 3 months after smoking. In heavy smokers, it can be detected for up to 1 year.
Dangers of Nicotine
Nicotine poses several health risks, including:
Increased Blood Pressure and Heart Rate Nicotine can raise blood pressure and increase heart rate.
Hardened Blood Vessels This increases the risk of heart and brain vessel blockages.
Addiction Nicotine is highly addictive, leading to regular smoking and exposure to over 7,000 harmful chemicals in cigarettes. This can cause chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), lung cancer, skin cancer, leukemia, esophageal cancer, nasal and oral cancer, liver cancer, and bladder cancer.
Pregnancy Risks For pregnant women, nicotine can affect the fetus, leading to premature birth, low birth weight, or, in severe cases, fetal death.

Blood Test
A blood test involves collecting a sample from a vein, which is then analyzed in a laboratory. This method is highly accurate but can be more expensive than a urine test.
Urine Test
A urine test is performed by collecting a sample in a dry, clean container. The sample is sent to a laboratory to detect nicotine and its metabolites, such as cotinine. This method is convenient for sample collection and cost-effective but is not suitable for long-term detection.
Saliva Test
A saliva test uses a test strip or collection tube for saliva samples, which are then analyzed in a laboratory. This method is convenient, non-invasive, and easy to collect samples, but it may be less accurate than a blood test.
Hair Test
A hair test involves collecting a hair sample, approximately 1.5 inches from the scalp, which is then analyzed in a laboratory. This method is suitable for long-term detection and is non-invasive, but it is relatively expensive and takes longer to get results.
Which Method is the Most Accurate?
The most accurate method for nicotine testing is the blood test.
Purpose Suitability of Each Method
Blood Test: Ideal for those requiring high accuracy.
Urine Test: A cost-effective method commonly used for pre-employment screening.
Saliva Test: Suitable for quick results and short-term detection, such as monitoring smoking cessation over 1-4 days.
Hair Test: Best for long-term detection, capable of finding nicotine even after an extended period of cessation.
Read More on Drug Testing: Why Test for Drugs? What Are the Methods?

Cost of Urine Nicotine Testing
The price of urine nicotine test is from 1,350 - 1,700 baht.
Who Should Get Tested?
Employees: Individuals whose workplace requires drug testing.
Pre-employment Screening: Those undergoing health checks before starting a new job.
Surgical Candidates: Patients advised by their doctors to undergo testing before surgery.

Individuals Quitting Smoking: People in the process of quitting smoking to monitor their progress.
Health Issues Related to Smoking: Those experiencing health problems from smoking or nicotine-containing devices.
Preparation for Testing
To prepare for nicotine testing, consider the following:
Avoid Foods Containing Nicotine: Refrain from consuming foods such as cauliflower, eggplant, tomatoes, and bell peppers for 2-3 days before testing. However, small amounts of these foods are unlikely to cause false positives.
Avoid Exposure to Cigarette Smoke: Steer clear of secondhand smoke and do not smoke cigarettes.
For Former Smokers: Drink plenty of water, eat foods rich in antioxidants (such as dark chocolate, berries, and pecans), and engage in regular exercise to help expedite the elimination of nicotine from your urine.

Summary
Nicotine testing is a process used to assess the use of nicotine-containing products, such as cigarettes and e-cigarettes. Nicotine can be detected in blood, urine, saliva, and hair. The blood test provides the highest accuracy, while urine tests are convenient and cost-effective, commonly used in health screenings. Saliva tests are non-invasive and suitable for short-term detection, whereas hair tests are ideal for long-term retrospective analysis.
"Nicotine testing offers numerous benefits, such as health assessments to evaluate health issues, monitoring smoking cessation, workplace compliance checks, and treatment planning. Choosing the appropriate testing method and preparing well can lead to accurate results that are beneficial for health management and medical diagnosis."
— NARADA PHIRATWISUT, MD. (General Practitioner at the Clinic) -
Reference documents
Chuanyi Mark Lu, MD, PhD,Nicotine and Cotinine Test
Pathology tests explained, Nicotine
How long does nicotine stay in your system?
Interesting articles
For more info and make appointment
Hot Line 081-562-7722
Compiled by NARADA PHIRATWISUT, MD.
Last Update : 26/09/2024
Usage Permission: Images may be used without permission strictly for educational or informational purposes, provided that credit is given, or the source is cited as intouchmedicare.com.
