What is gonorrhea? Treatment of gonorrhea in men and women by specialists, at an affordable price

HIGHLIGHTS
Gonorrhea is a Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD) caused by unprotected sexual contact and exposure to infected secretions through oral, vaginal, or anal intercourse. Some individuals contract genuine gonorrhea, while others may have conditions with similar symptoms, which can vary.
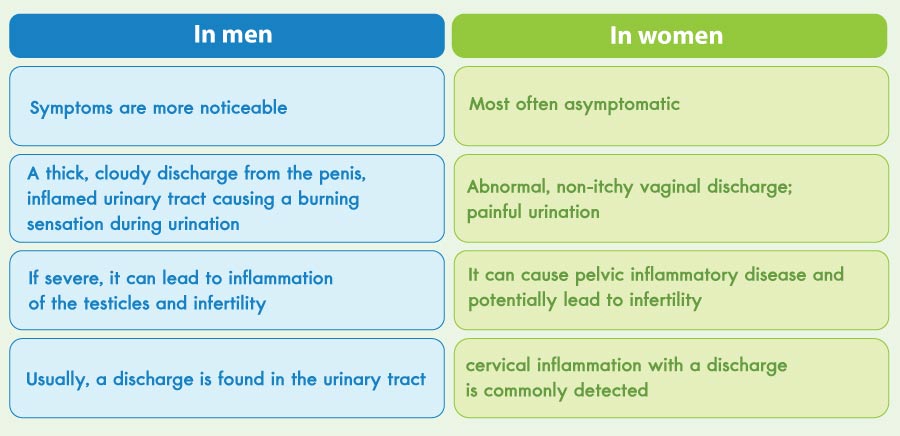
Common symptoms of gonorrhea in women include a burning sensation during urination, pain during urination, and abnormal colored or odorous vaginal discharge. In men, frequent symptoms are a burning sensation when urinating, pain during urination, and the discharge of white, yellow, or green pus from the penis.
Many wonder if gonorrhea can resolve on its own. It cannot; diagnosis and treatment by a medical professional are necessary. Treatment for gonorrhea may include injectable or oral medication, depending on the individual's symptoms. Successful treatment of gonorrhea requires patient cooperation. Affordable gonorrhea testing is available at local medical clinics near your home.
Related Knowledge on Gonorrhea
Where is the Best Place to Treat Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea can be treated at a nearby clinic or hospital. There, you'll find skilled doctors with experience, modern, standardized equipment, and prompt service without long waits at an affordable cost. Therefore, if you experience unusual symptoms, it is advisable to see a doctor rather than self-medicating to ensure correct and proper treatment.
If you are interested in inquiring more details or need treatment for gonorrhea or other sexually transmitted infections, you can search for "gonorrhea treatment clinic near me" on Google or contact Intouch Medicaire Clinic directly. Our friendly doctors and staff are ready to provide you with worry-free service. The treatment information is confidential and at a reasonable cost.
What are the risks associated with Gonorrhea
The risk of contracting or becoming infected with gonorrhea is significantly high if one has multiple sexual partners or engages in unprotected sexual activities, whether vaginally, anally, or orally. Additionally, individuals with a history of gonorrhea are at risk, as the infection can be transmitted even when symptoms are not yet present.
Currently, there is a rising trend in infection rates, and many people mistakenly believe that gonorrhea can resolve on its own. However, proper medical diagnosis and treatment are essential.
What does Gonorrhea look like in men?
In men, gonorrhea often presents with a burning sensation during urination and a discharge of cloudy pus from the urethra. The infection is commonly detected in the urethra and can sometimes lead to complications such as an abscess in the genital area or inflammation of the testicles.
What is Gonorrhea in women?
In women, gonorrhea is frequently asymptomatic, or it may cause abnormal, non-itchy vaginal discharge. If the infection worsens, it can spread to the uterus and fallopian tubes, leading to pelvic inflammatory disease, potential infertility, or an ectopic pregnancy. Oral sex can result in a gonococcal infection of the throat, often identified by inflammation and pus at the cervix.

Symptoms in women include:
Painful urination with discomfort;
Increased vaginal discharge that may have an unusual color or smell;
Vaginal bleeding between periods.

Symptoms in men include:
A burning sensation during urination
A white, yellow, or green discharge from the penis
Pain or swelling in the testicles (less common).

Discharge, bleeding
Itching around the anal region
A feeling of warmth or burning
Abdominal or rectal pain.
Picture of gonorrhea in women and picture of gonorrhea in men. Look at the example!!
If you notice any of the mentioned symptoms, you should consult a doctor and bring your sexual partner for testing as well. Moreover, if your partner has been diagnosed with gonorrhea, you should also get tested, even if you have no symptoms.
The manifestations of gonorrhea are as follows:
Asymptomatic gonorrhea
Approximately 50-90% of women and 10% of men infected with gonorrhea may show no symptoms at all.
Uncomplicated gonorrhea
Men typically experience urethritis with symptoms like painful urination and discharge. Women may suffer from cervical inflammation characterized by abnormal vaginal discharge and bleeding, accompanied by painful urination.
Anorectal infections often present no symptoms, but when they do, discomfort during bowel movements and discharge or bleeding from the rectum can occur.
Gonorrhea in the throat
This often shows no symptoms. A general sore throat or purulent throat might resolve on its own. However, if there’s a history of sore throat following oral sex, considering treatment for gonorrhea is also recommended.
Gonorrhea in the conjunctiva (eye infection)
Though rare, it can occur when the infection from the genital area spreads to the eye, leading to conjunctivitis or a pus-like discharge and potentially causing corneal ulceration.
Complicated gonorrhea
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) may occur, typically presenting with abdominal pain and high fever due to uterine or fallopian tube infection.
Disseminated gonococcal infection can lead to high fever and fatigue, and potentially more serious complications such as meningitis or endocarditis.
How much does a gonorrhea test cost
The price for a gonorrhea test ranges from 3,390 to 4,990 baht. The cost of treatment for gonorrhea depends on the symptoms and severity of the disease. There are specific packages for women interested in an internal examination and cervical cancer screening, which includes a gonorrhea test as well.
The causes of gonorrhea
Gonorrhea is caused by unprotected sexual intercourse or contact with the body fluids of an infected person. The infection primarily affects the genitals, anus, throat, and conjunctiva of the eyes.
How does gonorrhea spread
Gonorrhea spreads through vaginal, anal, or oral sex with an infected person. Pregnant women with gonorrhea can also transmit the infection to their babies during childbirth.a
How is genuine gonorrhea different from false gonorrhea
Genuine gonorrhea is caused by the Neisseria gonorrhoeae bacteria, with an incubation period of 2 to 5 days. In women, it can lead to inflammation of the urethra and cervix, resulting in discharge from the cervix. In men, it can cause a painful, inflamed, and burning sensation during urination, accompanied by discharge from the urethra.
False gonorrhea is caused by the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis and has a longer incubation period than genuine gonorrhea. It often presents with mild or no symptoms. Women may experience a yellowish discharge similar to leukorrhea, and the cervix may become swollen and red. Men may notice a yellowish stain on their underwear, with less severe symptoms than genuine gonorrhea but a tendency to become chronic if untreated.
Who should get tested for gonorrhea
Individuals recommended for regular gonorrhea testing include:
1. Those who engage in anal intercourse should consider annual screening.
2. Those who engage in vaginal intercourse are advised to get tested annually,
- especially if they are under 25 years old or over 25 with risk factors such as new or multiple sexual partners or a partner with a Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD)
If you engage in such behaviors, consult a doctor openly and honestly for accurate and precise testing for gonorrhea or other STD. ![]()
Ways to reduce the risk of gonorrhea
The only certain way to avoid gonorrhea or sexually transmitted infections is to abstain from all sexual activity, including vaginal, anal, or oral sex. However, if sexual activity cannot be avoided, the following practices should be adopted:
Have a single sexual partner who has been confirmed to be free of gonorrhea.
Use condoms correctly every time you have sex
If you have gonorrhea, can you still have sex?
You can resume sexual activities after completing a full course of antibiotics for gonorrhea and waiting an additional 7 days. It's recommended to avoid sex until you have finished treatment and the gonorrhea symptoms have disappeared to prevent reinfection.
Those with gonorrhea should get retested about three months after the initial infection treatment. Even if both partners have been treated, it's possible to get reinfected with gonorrhea. Despite proper treatment, prevention using condoms during sex is advised.
Can you have gonorrhea without seeing a doctor?
Not seeking medical treatment for gonorrhea can lead to serious and permanent health problems.
1. For women, untreated gonorrhea can lead to pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), which can cause complications such as:
Scar tissue formation blocking fallopian tubes
Ectopic pregnancy
Infertility
Chronic pelvic/abdominal pain
2. For men, gonorrhea can cause pain in the lower abdomen and may lead to infertility in some cases. Untreated gonorrhea can often spread to the blood or joints, which can be life-threatening.
Interesting Articles
References
Guidelines for the specific treatment of gonorrhea, Siriraj Medical Journal
Guidelines for the treatment of gonorrhea 2019, Department of Disease Control
Gonorrhea 2013, Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital, Mahidol University
Compiled by Renuka Maisuthisakul,MD.
Last Update : 20/11/2023