How much does an anti-influenza cost?

Price of anti-influenza medicine
Price: 1,250 per session (doesn't include doctor's fees, lab work, etc.)
- Price: 1,200 per session (doesn't include doctor's fees, lab work, etc.)
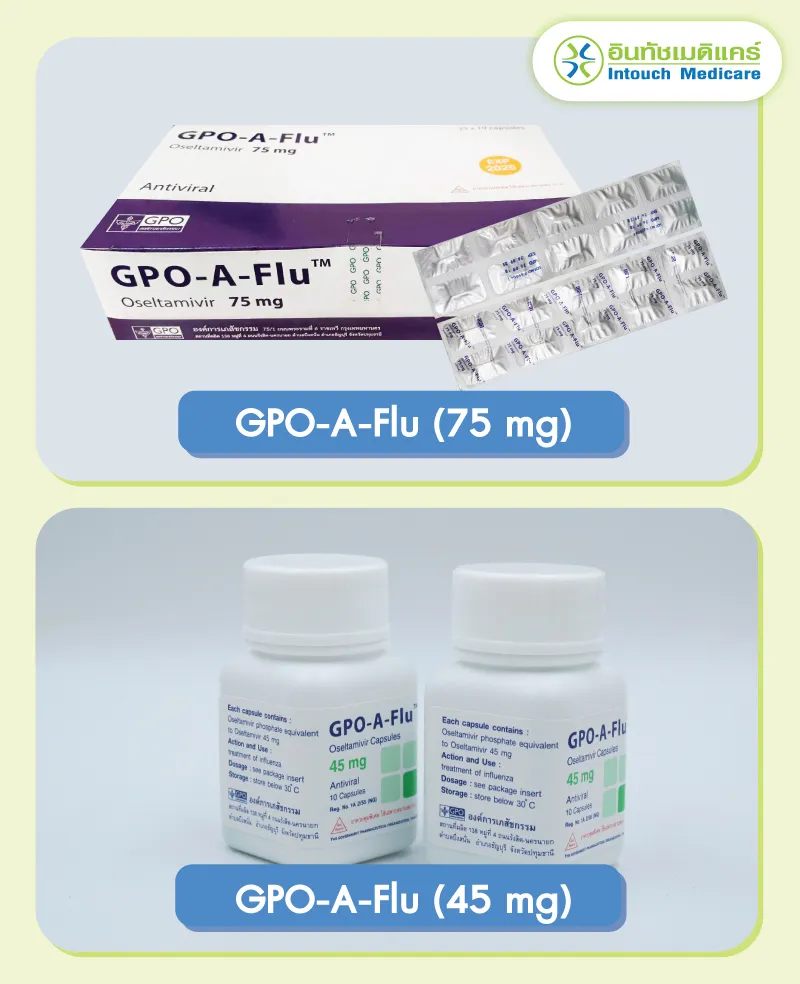
GPO-A-FU (oseltamivir)
Active ingredients
- In 1 capsule contains medicine Oseltamivir Phosphate is equivalent to oseltamivir 30 mg, 45 mg, and 75 mg.
Types of medicines
GPO-A-Flu (30 mg) white powder, packed in size 4 orange capsules. The capsule cap has the letters "OSEL" and the capsule body has the number "30".
GPO-A-Flu (45 mg) white powder, packed in green capsule number 4. Capsule cap has the letters "OSEL" and the capsule body has the number "45".
GPO-A-Flu (75 mg) white medicinal powder packed in capsule number 2, cream colored capsule. yellow cover
Indications for use
GPO-A-Flu It is used to treat and prevent infection with influenza viruses , either A or B, in adults and adolescents aged 13 years and older. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends the use of oseltamivir for the treatment of people involved in dissection. Poultry It is suspected that he may have been infected with influenza A virus from poultry (H5N1) in the respiratory tract.
medication dosage and how to use
Treatment of influenza A and B virus infections and influenza A virus infection from poultry.
Adults and adolescents 13 years and older : Take 75 mg twice daily for 5 days.
Children aged 1-12 years :
Body weight less than or equal to 15 kilograms: Take 30 mg 2 times a day for 5 days.
Body weight more than 15 kilograms - 23 kilograms: Take 45 milligrams each time, 2 times a day for 5 days.
Body weight more than 23 kilograms - 40 kilograms: Take 60 milligrams each time, 2 times a day for 5 days.
- Body weight more than 40 kilograms: Take 75 mg 2 times a day for 5 days.
note :
Medicine treatment should be started within 2 days of symptoms appearing. Influenza
For adults with a Creatinine clearance rate of 10-30 ml/min. Take 75 mg each time for 5 days.
Pharmacological and pharmacokinetic properties
Mechanism of action : Iseltamivir is an antiviral drug. which is a strong and specific inhibitor of enzymes Neuraminidase of the influenza virus This enzyme is important in the division of the Koi virus. It acts to cut Sialic Acid from Glycoconjugate. Causes viruses to be released from infected cells. Prevents virus aggregation after being released from the host cell and may reduce the virus-attenuating properties of respiratory secretions. When tested in vitro, oseltamivir is effective against both types of influenza virus. A and B, and this medicine is effective against influenza A virus from certain breeds of poultry. Iseltamivir was also effective against influenza A virus from poultry (H5N1 strain), which has been isolated. Obtained from patients in Vietnam and Thailand during 2004.
Pharmacokinetics : Oseltamivir is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract when administered orally as oseltamivir phosphate and is converted to active metabolites by hepatic esterases. At least 75% of the administered drug is absorbed into the bloodstream as active metabolites. The levels of active metabolites in the blood are highest within 2-3 hours after ingestion. They have an average distribution size of approximately 23 liters in humans. They bind to approximately 3% of plasma proteins. They have a half-life of 6-10 hours and More than 99% is excreted through the kidneys.
Contraindications for use of oseltamivir
Don't use in people allergic to oseltamivir. or other ingredients in this medicine
Precautions
Oseltamivir is excreted in breast milk in rats. In humans, it is not clear whether it will be excreted in breast milk or not. Therefore, it should be used with caution in women who are breastfeeding. And fever should only be treated when it is thought that the results of treatment are worth the potential risks to the baby.
Oseltamivir is not recommended for use in children under 1 year of age because the exact rate of growth of the blood-brain barrier in humans is not known and the toxicological data reported in Will the animal be clinically relevant to the infant?
Safety and pharmacokinetics in patients with hepatic impairment haven't been evaluated.
Dosage adjustment is recommended in patients with a creatinine clearance of 10-30 mL/min. Dosage adjustments are not applicable in patients with end-stage renal failure (eg, creatinine clearance less than 10 mL/min) and patients receiving hemodialysis. (Hemodialysis) or dialysis by inserting fluid into the peritoneal cavity (Peritoneal dialysis)
Postmarketing, there have been reports of self-harm and delirium in influenza patients taking oseltamivir. (Mostly occurring in Japan) Often reported in pediatric patients. It is not known whether oseltamivir Did it contribute to these events? Patients with influenza should be monitored for signs of abnormal behavior throughout treatment with oseltamivir. This is especially true during the first few days of treatment.

Use of the medicine in pregnant women and women during breastfeeding
Studies in rats have found that Oseltamivir is excreted into breast milk. It isn't known for sure whether oseltamivir is excreted in breast milk or not. Therefore, use of oseltamivir in breastfeeding mothers should only be used if the benefits are expected to be worth the risk of harm to the baby.
Side effects of anti-influenza medicines
Nausea do vomit or don't vomit, abdominal pain, diarrhea, nosebleeds. ear disease Conjunctivitis, dizziness, headache, insomnia, cough, dizziness and fatigue.
Overdose and treatment
There have been no reports of overdoses. However, the expected symptoms of acute overdose are nausea accompanied by vomiting or don't vomiting.
Favire (favipiravir)
Important active ingredients and dosage
Each tablet contains favipiravir. (favipiravir, INN : favipiravir) 200 mg
Types of medicines
Round, convex, yellow film coated tablets. One side has the letter "F", the other side is smooth.
Indications for use
Favire is indicated for new influenza virus infections or recurrent influenza virus infections. When currently available influenza antiviral drugs are ineffective or insufficiently effective

medication dosage and how to use
Take medication orally.
Adults: The dosage for favipiravir in adults is 1600 mg taken twice daily on day 1.
Then take a dose of 600 milligrams 2 times a day for another 4 days, with a total duration of using this medicine for 5 days.
Caution: This medicine should be used immediately. After starting to have flu-like symptoms
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamic properties
Antiviral activity in vitro: Favipiravir shows antiviral activity against influenza A and B viruses in the laboratory. with concentration value that gives an efficiency of 50% (EC50) equal to 0.014 - 0.55 micrograms/ml.
EC50 values for seasonal influenza A and B viruses and strains resistant to adamantane (amantadine and rimantadine), oseltamivir or zanamivir were 0.03 - 0.94 and 0.09 - 0.83 µg/mL, respectively.
EC50 value against influenza A virus (including strains resistant to adamantane, oseitamivir or zanamivi) such as swine flu and bird flu including highly pathogenic strains (including HIS5N1 and H7N9) equal to 0.06 - 3.53 µg/mL.
EC50 values for influenza A and B viruses resistant to adamantane, oseltamivir or zanamivir) were 0.09 - 0.47 micrograms/ml. and did not find cross-species resistance.
Pharmacokinetic properties
Drug absorption: The pharmacokinetic parameters of favipiravir are shown in the table in the package insert. After administering the drug to 8 healthy volunteers by taking the drug at a dose of 1600 mg 2 times a day for 1 day, then reducing the dose to 600 mg 2 times a day for 4 days, followed by 600 mg once a day again. 1 day (1600 mg/600 mg 2 times a day)

Contraindications
In women who are pregnant or suspected of being pregnant (Since it has been found to cause birth defects and death of early embryos in animal studies)
Patients with a history of hypersensitivity to any components of this medicine
Precautions for using medicine
This is because teratogenicity and early embryonic death were observed in animal studies of favipiravir. Therefore, don't use this medicine in women who are pregnant or suspected of being pregnant.
When to use favipiravir in women of potential pregnancy Confirm a negative pregnancy test result before starting treatment. Explain the risks and recommend effective birth control methods to those women's partners during treatment. and treatment has ended for 7 days. If pregnancy is suspected during treatment Stop treatment immediately and consult a doctor.
Favipiravir can be found in semen. When using this drug in male patients, the risks should be explained. and recommend effective birth control methods To have sexual intercourse during treatment and 7 days after treatment ends (men must wear condoms). Additionally, you should not have sex with pregnant women.
Before starting treatment Please explain the efficiency. and risk (including the risk of exposure to the fetus) in writing with the patient or family member and must receive written consent
Favipiravir should be used as necessary with caution

Use of the medicine in pregnant women and women during breastfeeding
Pregnant women : Favire should not be used by pregnant women. or suspect that you are pregnant (In studies of animals receiving doses similar to or lower than those used in clinical practice, It was found that the embryo died in the first stage. and toxicity to the fetus)
Women during breastfeeding: When favipiravir is given to women who are breastfeeding. It is recommended to stop breastfeeding. (The main metabolite of favipiravir is found in hydroxylated form in breast milk.)
Adverse reactions
1. Clinically important adverse reactions unusual behavior (incidence frequency unknown) : Although the causal relationship is unknown But abnormal behavior (such as running away suddenly Wandering around) can lead to accidents, trips and falls in patients infected with the influenza virus.
2. Clinically important adverse reactions (from similar medicines) The following clinically important adverse reactions have been reported. from using other influenza antiviral medicines Patients should be closely monitored. If any abnormal symptoms are found Treatment should be discontinued and appropriate corrective treatment given.
State of shock. Anapylachis.
Pneumonia
Severe and rapid hepatitis, liver dysfunction, diarrhea
Severe allergic skin reaction to toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN). oculomuco-cutaneous syndrome (Stevens-Johnson syndrome)
acute kidney injury
Decrease in the number of white blood cells, neutrophils, platelets.
Neurological and psychiatric symptoms (disturbed consciousness, delirium, hallucinations, delusions, confusion, etc.)
Inflammatory bowel disease, bleeding
3. Other adverse reactions If any of these adverse symptoms occur Appropriate treatment should be given according to symptoms.
Interesting Articles
Causes of Influenza symptoms you need to knows and how to treat
What are the differences between influenza symptoms and common cold symptoms?
Vaccine to protect against 4 strains of influenza (Influenza vaccine)
For more info and make appointment
Hot Line 081-562-7722
Composer : Intouchmedicare
Last edited : 21/05/2024

